What is Blood gas analyzer /ABG
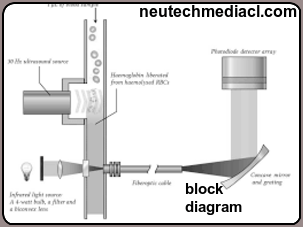
The main components of an NDIR sensor are an infrared source, a sample chamber, and an infrared detector. The IR light passes through the sample cell and the reference cell and reaches the detector. The reference chamber is filled with a gas, usually nitrogen.
What is Blood gas analyzer function
The gas that is measured is called the sample gas. This sample gas passes through the sample cell. A chopper motor is used to split the source IR rays to pass through both the sample and the reference cells.
To be more powerful must prevail in order for the lightning to be powerful in the cellulus, in the field of powerful electro-power. It is a state-of-the-art technology to implement this which is completely finished. What is Blood gas analyzer this is complete cover up.

Basic principle of Blood gas analyzer (ABG)
1. Measurement base of infrared gas analyzer
The Beer–Lambert law means that when a beam of parallel monochromatic light passes vertically through a uniform non-scattering light-absorbing material, its absorption is proportional to the concentration of the light-absorbing material and the thickness of the absorbing layer.
2. Infrared Gas Analyzer Working Principle(ABG)
The working principle of the gas analyzer is based on the selective absorption of infrared light by some gases. The commonly used infrared wavelength of infrared analyzer is 2~12μm.
Simply put, the gas to be measure is passes continuously through a container of a certain length and volume, and a beam of infrared light is injector from the side of one of the two end surfaces of the container that transmits light.

Then the intensity of the infrared radiation at the surface of the other end is measure and finally the gas concentration to be measure is know base on the absorption of infrared rays and the concentration of light-absorbing substances.
Advantage:
a) Wide measurement range:-The upper limit of the gas that can be analyze is up to 100%, and the lower limit is up to several (ppm) concentrations. After refined treatment, trace (PPB) analysis (analysis method in which the substance content is less than one part per million) can perform.
b) High sensitivity:- It has high monitoring sensitivity, and small changes in gas concentration can be distinguished.
c) High measurement accuracy:- Generally in FS (full scale). Compared with other analysis methods, it has high accuracy and good stability; Fast response speed: the response time is generally within 10S (time to reach T92).
3. Ultraviolet Blood Gas Analyzer Working Principle
Ultraviolet gas analyzer instrument is one of the visible spectrophotometer. Its analysis method is call ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy, and its working principle is base on the Beer–Lambert law.
Beer-Lambert Law A=lg(1/T)=Kbc
from them, A is absorption; T is the transmittance, which is the intensity of the transmitter light compare to the intensity of the incident light; K is the molar absorption coefficient, which is related to the nature of the absorbed material and the wavelength of the incident light; C is the concentration of the absorbed substance; b is the absorbent layer thickness.
When the light source, wavelength and sample cell thickness are determined, they are stabilized. At this time the intensity of the light transmitte through the sample is only relate to the concentration of the component being measure in the sample.
Advantages: simple operation, can measure SO2, NOx, HC1, NH3 and other gases.
4. Thermal Conductivity Gas Analyzer Working Principle:-
A thermal conductivity gas analyzer is a physical gas analyzer. It is based on the principle that different gases have different thermal conductivity and calculates the content of certain components by measuring the thermal conductivity of the mixed gas.
Advantages: The thermal conductivity analysis instrument has a simple structure, stable performance, low price and relatively mature technology. It applies a wide variety of gases and is a basic analytical tool.
5. Electrochemical Gas Analyzer Working Principle:-
The electrochemical gas analyzer is a chemical gas analyzer. It measures gas composition based on changes in the amount of ions or changes in current due to chemical reactions.
To improve selectivity, prevent contamination of the surface of the measuring electrode, and maintain electrolyte performance, a diaphragm structure is typically use.
Commonly used electrochemical analyzers include positioning electrolysis type and galvanic battery type.
Advantages: Small size, fast detection speed, accurate, portable, direct detection and continuous detection on site.
What is Blood gas analyzer do
The term “blood gas analysis” (BGA) is use for laboratory tests that relate to a patient’s acid-base balance and oxygen status. Oxygen status is assess using the partial pressure of O2 (pO2) and the hemoglobin oxygen saturation (sO2).
The partial pressure of O2 (pO2) is measure by amperometry, while that of SO2 is measure by co-oximetry. Blood gas analyzers that do not have an integrate co-oximeter report the SO2 estimated from PO and other parameters.

Potentiometry is use for pH and partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2) measurement. Other report parameters such as total CO2 (tCO2), bicarbonate concentration (cHCO3-), and base addition (BE) are calculate from the measure values.
What instrument is used to measure Blood gas analyzer/ABG
Current analyzers measure not only blood gas parameters but also electrolytes (PH, sodium, potassium, chloride, ionized calcium, ionized magnesium) and metabolites (glucose, lactate, bilirubin, creatinine). These additional analyzes are usually name “related measurements”. This must report within 30 minutes.
Emergency and intensive care departments use BGA as an essential part of an assessment of a patient’s clinical status. The stressful and hectic environment often increases the chances of errors manifold which may result in adverse patient outcomes.
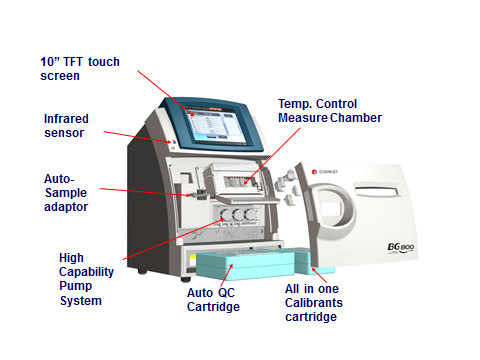
Achieving high levels of laboratory diagnostics of blood gases and related measurements requires standardization of ordering, collection and analysis.
Based on these key points and current global guidelines, WG BGT members made a joint effort in establishing recommendations for blood gas testing, which included the pre-analytical phase of blood gas testing, sampling procedures, BGA and quality control .
Due to the widespread use of Point of Care Testing (POCT) devices for blood gas testing, protocols relating to their use by non-laboratory personnel require special attention.
This document is divide in the following sections:
- Sample types used for blood gas analysis,
- Responsibilities in blood gas testing,
- Procedure for blood gas sampling, and
- Blood gas sample analysis.
1. The sample type is use for BGA.
Different types of samples are use for blood gas measurement – arterial blood, “arterized” capillary, “mixed” venous blood and venous blood. The physician should consider the patient’s condition, the benefits and limitations of different types of sampling when deciding on the most appropriate sample type and collection site.
2. Responsibilities in Blood Gas Testing
Arterial blood sampling should only perform by healthcare workers within the legal scope describe for their situation in their home country and who have demonstrate proficiency after formal training.
Medical doctors (MDs) should be able to independently sample arterial blood after graduation, based on the training and skill list for medical studies. This skill is improve during postgraduate study and specialization. Bachelor of Nursing is trainee in arterial blood sampling as order by MD.
A nurse has theoretical and practical knowledge in sampling other samples. Which are use in the analysis of acid-base status – samples of capillary and venous blood.
3. Procedure for Blood Gas Sampling
Sample preparation requires a pathology request form for patient identification, BGA. Included are rules related to patient evaluation, explanation of sample collection procedures to the patient, and blood gas sample labeling.
4. What is Blood Gas Analyzer Sample
BGA should be perform by trainee laboratory personnel. Complete training requirements should be document in laboratory standard operating procedures. Capacity assessment of employees responsible for BGA should be Carrie out for new employees and capacity reassessed annually.
Training and qualification records for all employees must be maintain in accordance with the requirements of good laboratory practice. What is Blood gas analyzer What is Blood gas analyzer this paragraph only SEO purpose What is Blood gas analyzer What is Blood gas analyzer
What is the Troubleshooting of Blood Gas Analyzer
Troubleshooting a blood gas analyzer machine requires a systematic approach to identify and address any issues that may arise during its operation. These machines are critical for monitoring a patient’s blood gas levels, so prompt and accurate troubleshooting is essential. Here is a step-by-step guide for troubleshooting a blood gas analyzer:
- Refer to the User Manual: Start by reading the manufacturer’s given user manual. It includes useful details about how the machine works, error codes, and model-specific troubleshooting techniques.
- Check Power and Connections: Make sure all wires and connections are tight and the machine is securely attached to a power source. Make sure the machine’s battery backup is charged or, if necessary, replace it.
- Inspect Reagents and Consumables: Verify the expiration dates and correct storage of the reagent containers, calibration solutions, and consumables. Any broken or expired parts should be replaced.
- Calibration: Perform a calibration if the machine prompts you to do so. Calibration ensures accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Error Messages and Codes: Pay attention to any error messages or error codes displayed on the machine’s screen. Refer to the user manual to interpret these codes and take appropriate action.
- Quality Control: Run quality control tests with known control samples to verify the accuracy and precision of the analyzer. If the results are out of range, recalibrate or troubleshoot as needed.
- Sample Handling: Ensure that the blood samples are properly collected, stored, and prepared according to the machine’s requirements. Check for air bubbles in syringes, proper mixing of samples, and adequate sample volume.
- Sensor Maintenance: Clean and maintain the sensors and electrodes as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Buildup of contaminants can affect the accuracy of readings.
- Software Updates: Check if there are any software updates available for the machine. Updating the software can sometimes resolve bugs or improve performance.
- Temperature and Environmental Conditions: Ensure that the machine is operating within the specified temperature and environmental conditions. Extreme temperatures or humidity can affect its performance.
- Service and Technical Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact the manufacturer’s technical support or a qualified service technician. They can provide remote assistance or schedule an on-site visit if necessary.
- Documentation: Maintain a log of troubleshooting steps taken, error messages, and any actions performed. This information can be helpful when seeking assistance from technical support.
FAQ
What does a blood gas Analyser do?
Typically, a blood gas analyzer examines the pH of the blood as well as the partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
What are the different types of blood gas analyzers?
A blood gas analyzer might be of two different forms. The dry blood gas analyser is one. the alternate variety of wet blood gas analysis, commonly known as a packet unit.
What is the name of blood gas analyzer?
The blood gas analyzer ABL80 FLEX
Ideal for glucosuria, electrolytes, and blood gas measurements in low- to mid-volume clinical settings.
What are the parameter of blood gas analyzer?
The following vital factors must be measured: pH, pCO2, pO2, Hematocrit Lactate, glucose, Na+, K+, and Ca++. It is best to measure each of these characteristics at the same time 3. Haemoglobin (cHgb), real bicarbonate (cHCO2), total carbon dioxide (cTCO2), and base excess in extracellular fluid should all be calculated parameters.
What is the principle of ABG?
ABG sensors monitor the hydrogen-ion concentration (pH), partial pressures of oxygen (PaO2), carbon dioxide (PaCO2), and the acid-base concentration (ABC), which is necessary for maintaining life.
What is a normal ABG value?
The following ABG component levels fall within an acceptable normal range: pointing out that the normal value range may varies between laboratories and in various age groups, from infants to geriatrics: pH (7.35-7.45) (75–100 mmHg) PaO2 (35–45 mmHg) PaCO2
Where is gas analyzer used?
They assist facility owners and managers in monitoring gas levels in their operations to make sure the numbers are within the acceptable range for the safety of employees and the quality of products and/or processes. They are used in a wide range of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and waste management.
Why is it called blood gas analysis?
The amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood are measured by blood gases. They also calculate the pH of your blood. A sample of blood is drawn from an artery using a needle for the blood gases test.
What is the full form of ABG analyzer?
What is the purpose of this examination? In order to determine how well your lungs are functioning, an arterial blood gas analysis (ABG) examines the ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide in your blood.