How to Read Prostate MRI
Multiparametric (Mp-MRI) imaging is a sophisticated imaging modality. It provides anatomical images and details on the operation of the prostate gland using three different MRI methods. Mp-MRI evaluates blood flow (also known as perfusion imaging) and the movement of water molecules (also known as water diffusion) inside the prostate.
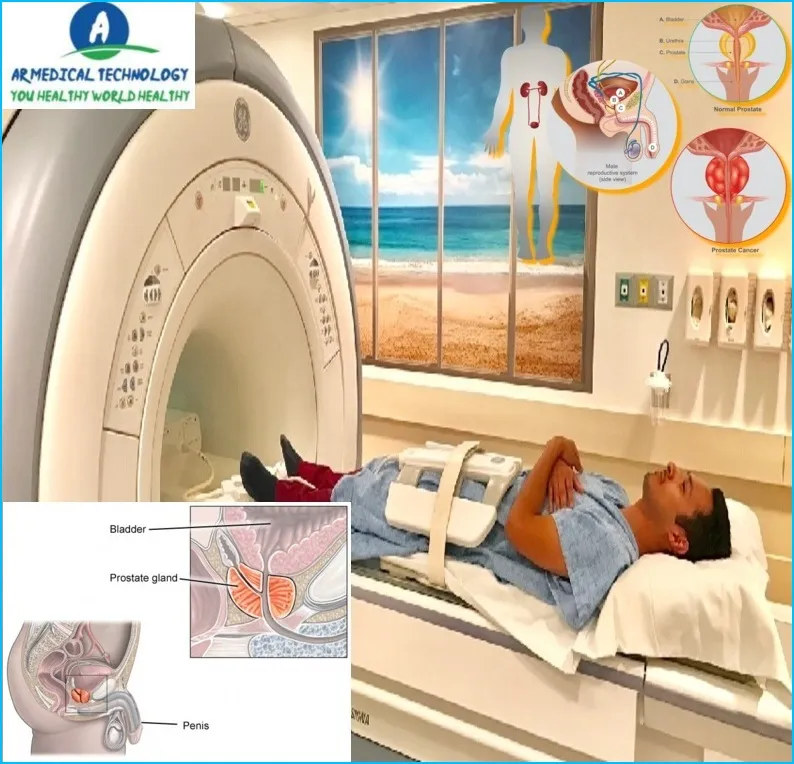
A diagnostic test for prostate cancer is prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A small camera is inserted into the rectum to capture pictures of the prostate as part of the examination. According to the American Cancer Society, one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis at some point in their lives. Prostate cancer is the most frequent cancer among males. Although the majority of prostate cancer cases are slow-growing and not fatal, a small percentage can be aggressive and spread quickly.

For this reason, routine screenings are crucial, particularly if you have a high risk of the condition. Topic: Five Smart Home Devices First of all, Everybody wants their houses to be as handy and pleasant as they can be. Luckily, there are many of devices available on the market that can assist us in achieving this objective. We examine five of the top devices for smart homes in this blog article. These gadgets, which range from voice-activated assistants to security cameras, will simplify your life and increase the safety of your house. Read on to find out more.
Prostate MRI
A diagnostic technique for assessing the prostate gland and associated components is prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). To acquire high-quality pictures, an endorectal coil—which is inserted into the rectum—is a feature of a specialized kind of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner.
Because prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may give precise information about the size, shape, and position of any worrisome lesions, it is frequently used to screen men who may have prostate cancer. Prostate MRIs can also be used to track a patient’s reaction to therapy or determine how far along a known prostate cancer has progressed.
An enema tube is inserted into the rectum to empty the colon prior to the prostate MRI examination. You will lie on your back on an exam table with your legs raised in stirrups for around 30 to 60 minutes during the test. To lessen motion artifacts throughout the exam, you might be requested to hold your breath for a brief period of time.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports

Prostate MRI Preparation
It’s critical to understand the exam’s potential outcomes and how to prepare for it if your doctor has advised a prostate MRI.
A four-hour fast is often required in order to prepare for a prostate MRI. Additionally, you will be required to retain your pee during the test and consume 32 ounces of water one hour prior to the MRI. MRIs often take between 30 and 60 minutes.
A radiologist will evaluate the results of your prostate MRI and communicate the findings to your physician. The results might be normal or show signs of an anomaly like a tumor or enlarged prostate.
If an anomaly is discovered, more examinations could be required to identify if it is malignant or benign. A biopsy may be advised in specific circumstances.
This article’s content aims to educate you on how to be ready for the exam and what to anticipate from a prostate MRI. Ask your physician or the radiology technologist who conducted the exam if you have any questions.
Prostate MRI Protocol
Before your prostate MRI, you will likely have a consultation with your doctor to discuss the details of the exam. You will then be asked to sign a consent form.
The next step is preparing for a prostate MRI, which may include drinking 32 ounces of water an hour before the exam and emptying your bladder just before the exam begins. For some men, an enema may also be part of the preparation.
During the exam, you will lie on your back on an exam table with your legs raised in stirrups. A small, gel-covered coil will be placed on your lower abdomen or rectum. This helps in improving the quality of the coil images.
The table will then slide into the center of the MRI machine, and images will be taken from different angles. The entire exam usually takes 30 to 60 minutes.
Prostate MRI Vs Biopsy
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The prostate produces a fluid that helps nourish and transport sperm. The urethra, which carries urine out of the body, runs through the center of the prostate.
Prostate MRI versus biopsy is a topic of great debate among doctors. Prostate MRI uses magnetic resonance imaging to create pictures of the inside of the prostate gland. During a biopsy, a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and examined under a microscope.
There are pros and cons to both procedures. Prostate MRI is less invasive than biopsy and does not require sedation or anesthesia. Additionally, MRI can provide more detailed images of the prostate gland than biopsy. However, MRI is more expensive than biopsy and is not always covered by insurance. A biopsy has a higher chance of detecting cancer cells than an MRI, but there is a risk of complications associated with the procedure, such as infection or bleeding.
The decision to have prostate MRI versus biopsy should be made after discussion with your doctor.
Multiparametric Prostate MRI
A multiparametric prostate MRI (mpMRI) is an imaging technique that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to examine the prostate. This type of MRI differs from a conventional MRI, which produces images of the body in only two dimensions. A multiparametric prostate MRI creates images of the prostate in three dimensions, which allows for more accurate diagnosis of prostate conditions.
The MPMRI procedure begins with the patient lying on their back on an examination table. A small instrument called an endorectal coil is inserted into the rectum, and this coil helps to produce clear images of the prostate. After this, the patient will have an MRI scan, which lasts for about 30 minutes. During the scan, the patient may be asked to hold their breath for a short time.
After the scan is complete, the images will be reviewed by a radiologist. The radiologist will look for abnormalities such as a tumor or swelling in the prostate gland. If anything suspicious is found, additional testing may be recommended.
Prostate MRI Radiology
Prostate MRI radiology is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. It produces a fluid that forms part of semen.
Prostate MRI uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to create detailed images of the prostate gland and surrounding tissue. MRI does not use ionizing radiation, so it is considered safe for pregnant women and children.
A prostate MRI exam usually takes 30-60 minutes. During the exam, you will lie on your back on an exam table with your legs raised in stirrups. A small device called a transducer will be placed in your rectum to help get clear images of your prostate gland. You may be asked to hold your breath for a short time during the test to avoid movement artifacts.
After the test, you can return to your normal activities right away. There is no recovery period or side effects associated with a prostate MRI.

Prostate MRI Results
If your doctor has recommended a prostate MRI, it’s important to understand how to read your results. Here’s a quick guide:
The first thing you’ll see on your results is a T2-weighted image. This image shows the size and shape of the prostate. The next image is the diffusion-weighted image (DWI). This image shows how well water molecules are moving through prostate tissue. The last image is the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map. This map shows how much water is in prostate tissue.
Prostate cancer usually appears as an area of abnormal tissue on one or more of these images. Your doctor will be able to tell if there are any areas of concern and discuss the next steps with you.
FAQ
What does an MRI show for prostate?
The movement of blood and water molecules through the prostate can be seen on an MRI. This aids in identifying the presence of cancer and, if so, its aggressiveness and extent of dissemination. An MRI of the prostate may occasionally be required to assess further prostate problems, such as an infection or abscess.
How much does a prostate MRI cost?
An MRI of the prostate might cost between $400 and $2,500. However, it can be greater based on your insurance and residence.
Can prostatitis look like cancer on MRI?
With low T2 signal intensity at T2WI, slight diffusion limitation on the ADC map, reduced citrate peaks and enhanced choline peaks, and considerable contrast wash-in and wash-out at DCE, chronic prostatitis may resemble prostate cancer at Mp-MRI.
Is prostate MRI Painful?
During the insertion, you should experience a slight pressure, but otherwise, you should be at ease during the examination.
Is MRI of prostate safe?
A prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive diagnostic procedure that produces comprehensive images of your prostate gland and surrounding tissues using radiofrequency pulses, a strong magnetic field, and a computer. It uses no radiation and is usually painless and safe.
Why would urologist want MRI of prostate?
Prostate MRI makes it possible to locate, identify, estimate the volume, and evaluate the extent of the tumor. This data, when paired with the outcomes of focused biopsies, allows for the precise mapping of prostate cancer and more customized treatment care for individual patients.









