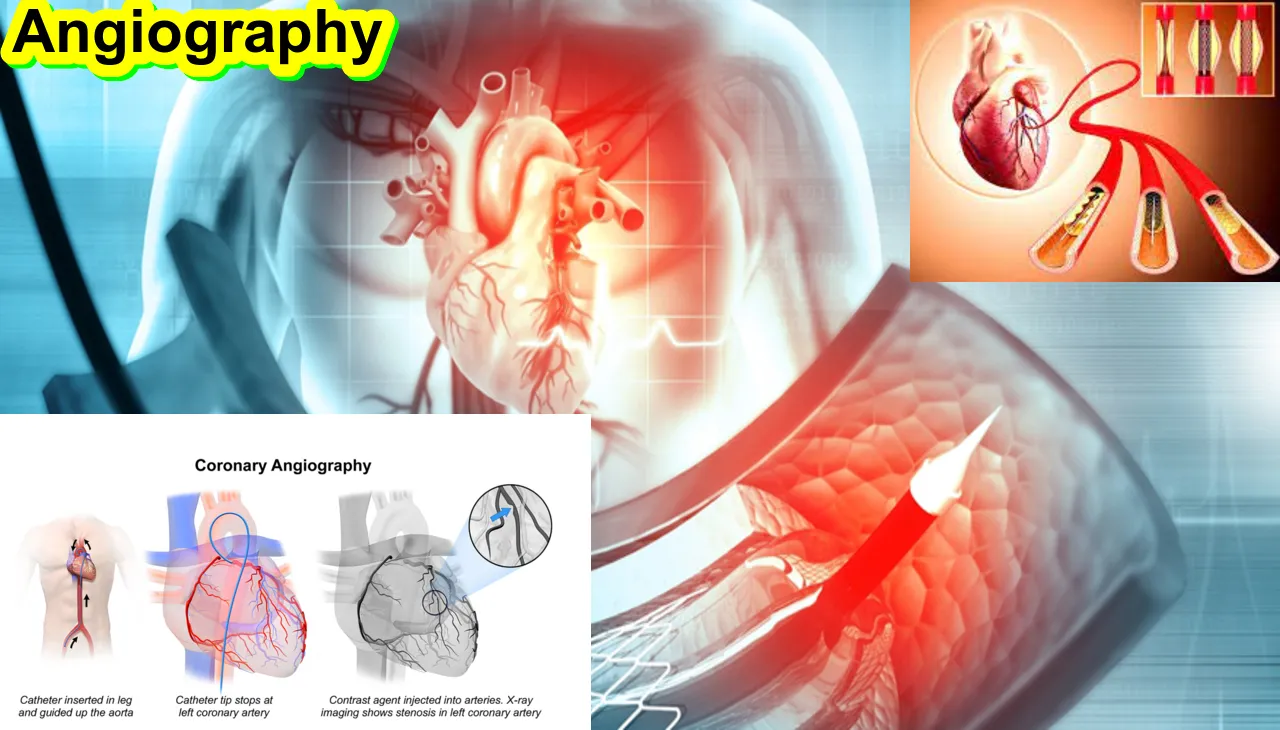
What is Angiography
An X-ray technique called angiography is used to examine blood arteries. Because blood vessels are not visible on a standard X-ray, your blood must first be infused with a special dye known as a contrast agent. This makes your blood vessels more visible, so your doctor can notice any issues.
Angiography is a medical imaging method that shows the body’s blood vessels, including veins and arteries. This diagnostic process aids medical practitioners in evaluating blood flow, locating obstructions, spotting irregularities, and formulating treatment plans for vascular disorders. Obtaining fine-grained pictures of the circulatory system is the common objective of several angiography methods.
An outline of angiography is provided here:
1. Types of Angiography:
- Conventional Angiography: In this traditional form, a contrast dye is injected directly into the blood vessels, and X-rays are taken to capture real-time images. This method provides high-resolution images but involves some level of invasiveness.
- CT Angiography (CTA): This technique uses computed tomography (CT) scanning to generate detailed images of blood vessels. A contrast dye is often injected intravenously, and the CT scanner captures cross-sectional images.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize blood vessels. Similar to CTA, a contrast agent may be injected to enhance image quality.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): DSA involves the use of X-rays and a contrast dye to create detailed images of blood vessels. It subtracts a pre-contrast image from images taken after contrast injection, highlighting the vessels.
2. Procedure:
- Preparation: Before the angiography procedure, the patient may be asked to fast for a certain period. In some cases, a sedative may be given to help the patient relax.
- Contrast Injection: A contrast dye is injected into the blood vessels through a catheter (a thin, flexible tube). The catheter is often inserted through a small incision, usually in the groin area, and guided to the target vessel using fluoroscopy or other imaging techniques.
- Imaging: Once the contrast dye is injected, the imaging procedure begins. X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans capture detailed images of the blood vessels, highlighting their structure and any abnormalities.
- Post-Procedure: After the imaging is complete, the catheter is removed, and the incision site is typically closed with a small stitch or closure device. Patients are monitored for a brief period to ensure there are no complications.
3. Applications:
- Diagnosis: Angiography helps diagnose conditions such as arterial blockages, aneurysms, and vascular malformations.
- Treatment Planning: It assists in planning interventions, such as angioplasty or stent placement, to improve blood flow in blocked or narrowed vessels.
- Monitoring: Angiography is used to monitor the progression of vascular diseases and the success of interventions over time.

How to work Angiography
A number of procedures are involved in performing angiographe in order to view blood arteries and evaluate their health. Depending on the type of angiography that is being performed—conventional, CT, magnetic resonance, or digital subtraction angiography (DSA), for example—the process may change. An outline of the steps in the angiography procedure is provided below:
1. Patient Preparation:
- Medical History: Obtain a detailed medical history from the patient, including any allergies, history of kidney problems, or previous reactions to contrast dye.
- Consent: Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
- Fasting: In some cases, patients may be instructed to fast for a certain period before the procedure.
- Pre-procedure Medications: Administer any necessary pre-procedure medications, such as sedatives to help the patient relax.
2. Insertion of Catheter:
- Access Site: Choose an appropriate access site for catheter insertion, often in the groin or arm.
- Local Anesthesia: Administer local anesthesia to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted.
- Catheter Insertion: Insert a catheter through a small incision or puncture site. The catheter is guided through blood vessels using fluoroscopy or other imaging techniques.
3. Contrast Injection:
- Positioning: Ensure the catheter is in the desired position near the area of interest.
- Contrast Injection: Inject a contrast dye through the catheter into the blood vessels. The contrast dye helps visualize the blood vessels during imaging.
4. Imaging:
- Real-time Monitoring: Use imaging modalities such as X-rays (conventional angiography), CT scans (CTA), or MRI scans (MRA) to monitor the real-time flow of contrast dye through the blood vessels.
- Capturing Images: Capture images at various angles and positions to obtain a comprehensive view of the blood vessels.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): In the case of DSA, obtain pre-contrast images and subtract them from post-contrast images to enhance the visibility of blood vessels.
5. Post-Procedure:
- Catheter Removal: After imaging is complete, carefully remove the catheter.
- Closure of Puncture Site: Close the incision site with a small stitch or use a closure device, depending on the procedure and facility protocols.
- Patient Monitoring: Monitor the patient for a brief period to check for any immediate complications or adverse reactions.
6. Post-Procedure Care:
- Hydration: Encourage the patient to stay hydrated to help flush the contrast dye from the body.
- Observation: Monitor the patient for any delayed reactions or complications.
7. Results and Reporting:
- Interpretation: The obtained images are interpreted by a radiologist, and a report is generated.
- Communication: Communicate the findings with the referring healthcare provider for further diagnosis and treatment planning.
What is the procedure for Angiography?
In angiographe, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin, arm, or neck and carried through the blood vessels to the heart. A coronary angiogram can show blocked or narrowed blood vessels in the heart. Coronary angiogram uses X-ray imaging to view the blood vessels of a patient’s heart. ct angiogram, coronary angiography,
What is the risk of angiography?
Although angiographe is typically regarded as a safe and well-tolerated technique, there are always certain inherent hazards associated with any medical intervention. It’s crucial to remember that, in terms of identifying and treating vascular disorders, angiography frequently has advantages over disadvantages. The following are some possible dangers connected to angiography:
- Allergic Reaction to Contrast Dye:
- One of the primary risks is an allergic reaction to the contrast dye used during angiographe. This can include symptoms such as hives, itching, or, in rare cases, more severe reactions like difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. Patients with a history of allergies or previous reactions to contrast dye may be at a higher risk.
- Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN):
- Contrast-induced nephropathy is a condition where the contrast dye can cause kidney damage, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney problems. Adequate hydration before and after the procedure is often recommended to minimize this risk.
- Bleeding or Hematoma:
- There is a risk of bleeding or the formation of a hematoma (a collection of blood outside blood vessels) at the catheter insertion site. This risk is higher in patients on blood-thinning medications or those with certain bleeding disorders.
- Infection:
- While rare, there is a risk of infection at the catheter insertion site. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize this risk, such as using sterile techniques during the procedure.
- Vessel Damage:
- There is a small risk of damage to the blood vessels during catheter insertion. This can lead to complications such as dissection (tearing) of the vessel or the formation of a blood clot.
- Radiation Exposure:
- Procedures like conventional angiography that use X-rays expose patients to ionizing radiation. The amount of radiation is generally considered safe, but repeated exposure may increase the cumulative risk, especially in sensitive populations.
- Dislodgment of Plaque or Blood Clot:
- The manipulation of catheters within blood vessels during angiographe can potentially dislodge plaque or blood clots, posing a risk of embolism. This risk is usually minimized through careful procedural techniques.
- Stroke or Other Neurological Complications:
- In rare cases, there is a risk of neurological complications, such as stroke, during angiographe. This risk is higher in certain procedures, especially those involving the blood vessels in the neck or brain.
How Is angiography a surgery
Angiographe is a usual medical procedure use to visualize blood flow within the nervous system. It may be important to diagnose various medical conditions.

Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
What is the reason for angiography?
An angiographe can show doctors what’s wrong with a patient’s blood vessels. It shows how many coronary arteries are blocked or narrowed by fatty plaques (atherosclerosis), indicating where the blockages are located in the patient’s blood vessels.
Angiographe is used to examine the health of blood vessels and how blood flows through them. It helps diagnose a number of problems affecting the blood vessels, mainly including: Atherosclerosis – narrowing of the arteries, which means you are at risk of stroke or heart attack.
When is angiography required?
The doctor may recommend a coronary angiogram if there are signs of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain (angina), pain in the chest, jaw, neck, or arm that cannot be explained by other tests. New or increasing chest pain (unstable angina) etc. Then recommend to do angiographe.
How serious is angiography?
Angiographe is generally a safe procedure, but there may be minor side effects and a small risk of serious complications. The patient will have the procedure only if the benefits outweigh any potential risks. Talk to your doctor for more information about the risks of having angiographe.
Advantages of Angiography
Heart and vascular CT angiography can eliminate the need for surgery. If surgery remains urgent, it is performed more precisely. Heart and vascular CT angiography detects narrowing or blockage of blood vessels allowing potentially corrective therapy.
What are the disadvantages of angiography?
The dye can cause kidney damage, but this is usually temporary. Heart attack or stroke. Damage to a blood vessel, causing internal bleeding, may require further surgery to repair the damage. A severe allergic reaction to the dye (anaphylaxis), causing dizziness, difficulty breathing, or loss of consciousness.
What is the cost of Angiography test?
The average cost of angiograph is around $400-450, with prices varying depending on hospitals in different cities.

FAQ
What is angiography procedure?
One kind of X-ray used to look at blood arteries is called an angiographi. Because blood vessels are difficult to see on standard X-rays, an additional dye is injected into the region that needs to be studied. As the dye passes through the blood arteries, it illuminates them. This is known as a catheter angiography in medical parlance.
Is angiography very painful?
When a long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter is carefully directed to the area being inspected, it may push and pull on you, but it shouldn’t hurt. The procedure takes place in the artery.
How many hours angiography takes?
It takes one to two hours to complete the angiographi. It might take longer at times. In certain instances, the interventional radiologist performs a supplementary procedure, such an angioplasty, concurrently with the angiography. The process takes longer as a result.
Is life normal after angiography?
Most patients who have a coronary angioplasty with stents are able to resume their regular activities in a few of weeks.
Are you awake during angiography?
What is involved in a traditional coronary angiographi? Most of the time, it takes 20 to 30 minutes, and you won’t need to spend the night in the hospital. In what seems to be an X-ray room, the catheter lab is where you are lying down, comfortable, and awake.
What is the cost of CT angiography?
The cost of a CT angiographi test in Delhi often varies based on the diagnostic facility, from INR 8000 to INR 15,000.
What is angiography and cost?
The price range for coronary angiographi in India is between ₹ 12,000 and ₹ 22,000 (or INR 12,000 and INR 22,000). Nonetheless, the cost of an angiography or angiography test varies throughout India among private institutions located in various locations.
What is the maximum age for angiography?
Although angioplasty is safe to perform at any age, its hazards increase after the age of 80.









