How to work Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
Hear to pronunciation.( puh- LIH- meh- shafts chayn ree- AK- duck) A laboratory system used to make numerous clones of a specific piece of DNA from a sample that contains veritably bitsy quantities of that DNA.
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR is used to make millions of clones of a target piece of DNA. It’s an necessary tool in ultramodern molecular biology and has converted scientific exploration and individual drug.

What’s a Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR test?
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR. It’s a test to descry inheritable material from a specific organism, similar as a contagion.
The test detects the presence of a contagion if you have the contagion at the time of the test. The test could also descry fractions of the contagion indeed after you’re no longer infected
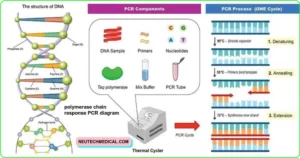
The PCR fashion is grounded on the enzymatic replication of DNA. In PCR, a short member of DNA is amplified using manual intermediated enzymes.
DNA Polymerase synthesizes new beaches of DNA reciprocal to the template DNA. The DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide to there-existing 3′- OH group only.
Explain the difference between KPCR and QPCR
QPCR is quantitative in nature, while RT- PCR is not. RT- PCR can be used without qPCR, for illustration to enable molecular cloning, sequencing or simple discovery of RNA.
Again, qPCR can be used without RT- PCR, for illustration to quantify the dupe number of a specific piece of DNA.
The main difference between PCR and qPCR is that PCR is a qualitative fashion whereas qPCR is a quantitative fashion.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) allows reading the result as “ presence or absence’. But in qPCR, the quantum of DNA amplified in each cycle are quantified
RT- PCR is used to amplify the reversed recap of the DNA law; QPCR measures the modification. 3. RT- PCR is for modification, while qPCR is for quantification.
In one- step RT- qPCR, cDNA conflation and qPCR are performed in a single response vessel in a common response buffer. In two- step RT- qPCR, cDNA is synthesized in one response, and an aliquot of the cDNA is also used for a posterior qPCR trial.
Explain why Viral cargo
What Is Viral cargo? It’s simply the quantum of contagion croakers can find in your body. They might use blood, nasal hearties, or other fleshly fluids to test the cargo for a particular contagion.
People infected with the coronavirus that causes COVID- 19 may have different viral loads.
What are the three process involved in during Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
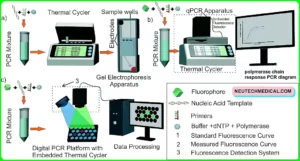
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is grounded on three simple way needed for any DNA conflation response
( 1) denaturation of the template into single beaches
( 2) annealing of manuals to each original beachfront for new beachfront conflation
( 3) extension of the new DNA beaches from the manuals.
Denaturing – when the double- stranded template DNA is hooted to separate it into two single beaches. Annealing – when the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA manuals to attach to the template DNA.
Extending – when the temperature is raised and the new beachfront of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme.
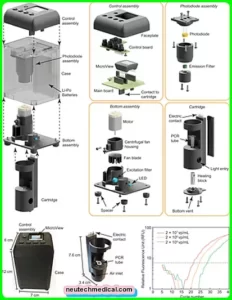
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) process has 4 stepscollection, medication, modification, and post PCR clean- up. The PCR machine way be in the modification step.
It begins with a member of a DNA sample placed in a suitable tube along with the reagents and chemicals listed above.
Operation of Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
We present a check of the following operations of PCR
1) The modification of gene fractions as fast volition of cloning.
2) The revision of DNA fractions.
3) The sensitive discovery of pathogenic microorganisms, if asked followed by an accurate genotyping.
4) DNA analysis of archaeological samples.
PCR is used in numerous exploration labs, and it also has practical operations in forensics, inheritable testing, and diagnostics.
For case, Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR is used to amplify genes associated with inheritable diseases from the DNA of cases( or from fetal DNA, in the case of antenatal testing)
Medical, forensic, and applied lores. In addition to introductory exploration, PCR- grounded technologies are used every day in clinical diagnostics, forensic examinations, and agrarian biotechnology.
These operations bear dependable performance, superb perceptivity, and strict specifications.
What are the factors which can affect viral cargo dimension.
Vaccinations, similar as a flu poke, and infections can beget a temporary increase in your viral cargo.
Talk to your croaker about whether you should delay your coming viral cargo test-occasionally it’s recommended to stay at least one month after having a vaccination or getting over an infection.
- An increase in viral cargo can do for numerous reasons, similar as.
- not taking antiretroviral drug constantly.
- the HIV has shifted( changed genetically).
- antiretroviral drug is not the right cure.
- a lab error passed.
- having a concurrent illness.
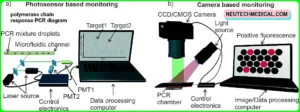
- There are three main tests used to measure viral cargo. These are rear recap- polymerase chain response( RT- PCR) tests, fanned DNA( bDNA) tests, and nucleic acid sequence- grounded modification( NASBA) tests.
What’s annealing Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
Annealing – when the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA manuals to attach to the template DNA.
Extending – when the temperature is raised and the new beachfront of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme.
At the annealing step of the PCR response the manuals interact with the template. In lower temp a partial match between the manual and the template will be stable enough and you would get modification from further places.
The annealing step is the PCR step in which the manuals anneal, or attach, to the DNA template. The third step in a PCR cycle is the extension step.
The extension step, also appertained to as the extension step, is the PCR step in which Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to the annealed manual.
What’s DNA denaturing
DNA denaturation is a process of separating dsDNA into single beaches, which are favorable to DNA hybridization. Indeed though the denaturation is a crucial response that determines the success of DNA hybridization grounded bioassays, no methodical characterization of denaturation system for dsDNA has been tried therefore far.
When a DNA result is hotted enough, the double- stranded DNA unwinds and the hydrogen bonds that hold the two beaches together weaken and eventually break.
The process of breaking double- stranded DNA into single beaches is known as DNA denaturation, or DNA denaturing.
Denaturation/ melting- the process of separation of double- stranded DNA into single beaches.( The process of separating the polynucleotide beaches of duplex nucleic acid.)
What’s the function of glamorous beds during Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
Genomic DNA insulation glamorous globules are used to separate genomic DNA from proteins and RNA from crude excerpt.
The optimization of swab, pH and charge in result permits just the genomic DNA to bind globules which can also be placed in a attraction for separation.
Overview of glamorous blob- grounded DNA birth using Sera- Mag globules. After binding DNA, an external glamorous field attracts the globules to the external edge of the containing tube, prostrating them.
While the globules are paralyzed, the blob- bound DNA is retained during the washing way.
What’s glamorous blob DNA sanctification? glamorous blob- grounded sanctification uses paramagnetic globules with functionalized silica shells to widely bind DNA.
The set DNA can also be fluently separated from the waterless phase with a attraction.
What are the manuals.
PCR manuals are short pieces of single- stranded DNA, generally around 20 nucleotides in length. Two manuals are used in each PCR response, and they’re designed so that they adjoin the target region( region that should be copied).
The conflation of a manual is necessary because the enzymes that synthesize DNA, which are called DNA polymerases, can only attach new DNA nucleotides to an being beachfront of nucleotides.
The manual thus serves to high and lay a foundation for DNA conflation.

Two manuals, forward manual and rear manual, are used in each Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR response, which are designed to adjoin the target region for modification.
Two reciprocal single beaches of DNA are released during denaturation.
Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3′- OH group, it needs a manual to which it can add the first nucleotide.
This demand makes it possible to delineate a specific region of template sequence that the experimenter wants to amplify.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) TEST KITE
Test your covid19 homemade easy to use and environmental friendly