What is mammography?
A mammogram is a low dose X-ray Radiation of breast tissue. Your healthcare provider uses mammograms or mammography to look for early signs of breast cancer before cancer symptoms develop. It is also called a screening mammogram. If you develop any new symptoms, such as a lump, pain, nipple discharge, or breast skin changes, your provider may use mammography to look for any abnormalities. It is also called a diagnostic mammogram.
Aside from skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common cancer that affects women from birth and represents 14% of all new cancer diagnoses worldwide and in the United States. While breast cancer treatment therapies continue to improve and have contributed to the reduction of cancer-related deaths, early diagnosis through screening mammograms has a greater overall impact on survival rates.
Most findings on a mammogram are benign or noncancerous. Fewer than 1 in 10 people needing additional tests after a mammogram turn out to be cancer.
How does a mammogram work?
A mammogram uses an X-ray machine that is designed to view breast tissue only. The mammogram machine takes a lower dose of X-rays than the X-rays used to look at your bones.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
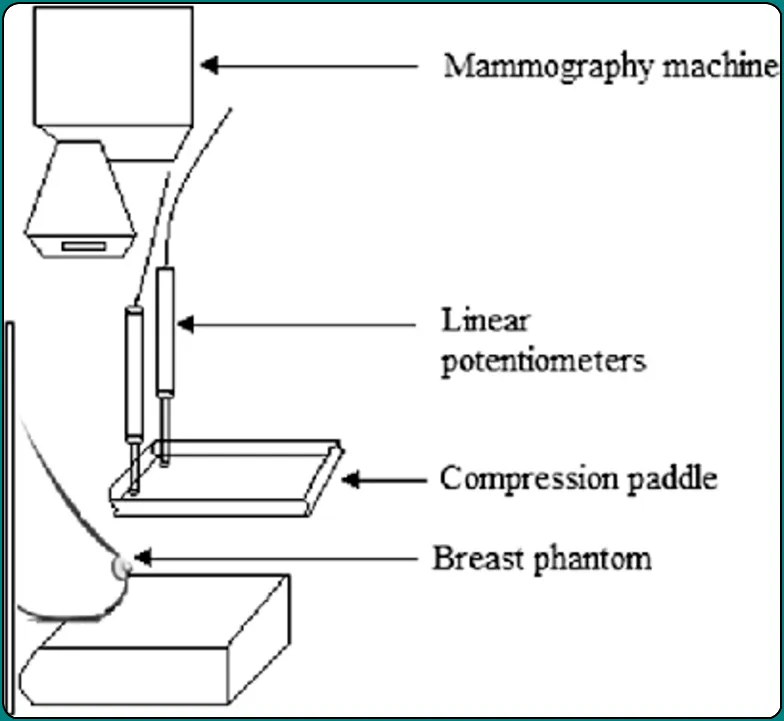
During a mammogram, you should position your breast properly on the support plate attached to the X-ray machine so that the image is not blurred. A technologist then positions your breast with parallel plates called paddles. The machine produces X-rays that travel from your breast to a detector located on the opposite side. The detector transmits an electronic signal to a computer to produce a digital image. These images are called mammograms.
Breast compression is necessary for a mammogram to keep your breast stable and reduce movement, which can make X-rays appear blurry. Compression also equalizes the shape of your breast so that the X-rays travel a shorter path to reach the detector. This allows less radiation and improves image quality.
What are the Different Types of Mammogram?
Digital mammography in 2D.
Digital mammography (digital breast tomosynthesis) in 3D.
Digital mammogram / Screening Mammogram
Digital mammography has replaced traditional (film) mammography, also known as analog mammography. Both digital and conventional mammography use X-rays to create an image of your breast. The only difference is that in traditional mammography the image is stored directly on film, while digital mammography provides an electronic image that is stored as a computer file. Digital mammography allows service providers to save the file electronically and to more easily evaluate and share images.
A digital mammogram usually includes at least two pictures of each breast taken at different angles, usually from top to bottom and from side to side, and provides a two-dimensional (2D) view.
3d mammogram/ diagnostic mammography
Here 3D mammography, also known as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), is a new type of mammogram in which each breast is compressed once and a machine takes low-dose X-rays as it moves around your Runs in an arc over the breast. A computer then puts the images together, which allows healthcare providers to see your breast tissue more clearly in three dimensions.
Several studies have shown that 3D mammography provides accurate data in cancer detection, including low-grade cancers, and decreases false-positive rates. Given these advantages, 3D mammography is fast becoming the preferred alternative to mammograms for both screening and diagnostic mammograms.
What is the difference between a screening mammogram and a diagnostic mammogram?
A screening mammogram is a routine mammogram your healthcare provider may order to look for signs of cancer or abnormal breast tissue before you have symptoms. Screening mammography helps you find breast cancer early. Early detection allows for early treatment, which proves to be more effective than when the cancer is found at a later stage.
A routine screening mammogram involves at least two pictures of each breast taken at different angles, usually from top to bottom and from side to side. If you have breast implants, you need additional images.
Your healthcare provider orders a diagnostic mammogram if a screening mammogram shows abnormal tissue or if there is a new breast problem.
While both types of mammograms use the same type of machine, diagnostic mammographi uses additional imaging techniques, such as spot compression, complementary angle or magnification views, and is supervised by a radiologist at the time of the study.
Can Mammograms Detect Cancer?
Mammograms can only help find cancer, but they cannot diagnose cancer. While mammograms can show abnormal breast tissue, they do not prove that an abnormal area in your breast is cancer. Instead, mammograms are an essential tool to help your healthcare providers decide whether you need additional testing, such as a breast biopsy. A breast biopsy can determine whether the tissue is cancerous or noncancerous.
At what age should a mammogram be done?
Several organizations, including the USA Cancer Society and the College of Radiology, recommend annual screening mammograms starting at age 40 for all people at average risk of developing breast cancer, from birth to a woman. Average-risk AFAB people are those with a lifetime risk of less than 15% of developing breast cancer. Your individual risk of a new breast cancer increases as you age.

People with AFAB who are at increased risk of developing breast cancer may need to have screening mammograms at a younger age because they may develop breast cancer at an earlier age. Your healthcare provider may recommend complementary screening with other tests, such as a breast MRI, based on your breast cancer risk assessment.
Occasionally, it has been observed that males at birth (AMAB) may also have higher risk levels due to their family history and screening mammographi. In general, though, about 1 in 100 people with AMAB get breast cancer.
If you have any of the following risk factors, talk with your healthcare provider about when you should begin annual screening mammograms:
- Personal history of breast cancer.
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer from birth.
- Inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Certain benign (non-cancerous) breast diseases such as atypical ductal hyperplasia and/or lobular neoplasia.
- Dense breasts.
How accurate is mammography?
Mammographi is 88% to 92% accurate. Mammograms have improved in their ability to detect breast abnormalities before they become large enough to be felt. It’s possible that a mass you can feel won’t show up on a mammogram. Any abnormality you feel when examining your breasts should be evaluated by your healthcare provider. They may recommend a diagnostic mammogram.
Who does mammograms?
A healthcare provider called a radiology technologist or mammographer performs the mammogram. She has a special diploma and training in performing mammograms safely and correctly. A certified radiologist from a recognized university who is specially qualified to interpret mammograms then views and interprets the mammogram images. They send the results to your healthcare provider who will share them with you.
Mammogram near me
How to prepare for mammogram?
There are a few things to keep in mind when scheduling your mammogram.
- If you are breastfeeding, pregnant or think you may be pregnant, tell your doctor. Your provider may suggest a breast ultrasound instead.
- If you experience menstruation, try not to schedule your health care provider right before your period or during your period. Your breasts may be tender during this time, which can make the procedure more uncomfortable.
- If you have had breast implants or have recently received a vaccine, be sure to tell the scheduler.
On the day of your mammogram, follow these guidelines
- Follow your normal routine – eat, drink and take your normal medicines.
- Do not apply deodorant, perfume, lotion or body powder on that day. These products may interfere with the accuracy of X-ray images.
- Some people choose to wear a top and bottoms instead of a dress on the day of their mammogram, which will require you to remove clothing above your waist for the imaging procedure. You will have a medical gown or drape to wear.
What should I expect during a mammogram?
- You should remove all clothing and jewelry above the waist. The provider will give you an open-front hospital gown or cloth to wear.
- You stand in front of the mammographi machine, and the technologist will ask you to remove your gown one breast at a time. Place your breast on the breast support plate.
- The technologist will lower a plastic paddle to press your breast against the support plate. You may feel some discomfort or pressure during the 3- to 5-second period of compression. If you are unable to tolerate the pressure, let the technologist know and they will adjust accordingly.
- The machine will take an X-ray of your breast while compressing it.
- Once the technologist has finished taking the X-ray with the machine, the procedure will end
What are the benefits of mammogram screening
Mammogram screening, which is a type of X-ray imaging of the breast, is a valuable tool for the early detection of breast cancer in women. Here are some of the key benefits of mammogram screening:
- Early Detection of Breast Cancer:
- Mammograms are effective in detecting breast cancer at an early stage, often before it causes symptoms or can be felt during a clinical breast examination. Early detection allows for more successful treatment and improved outcomes.
- Increased Survival Rates:
- Early detection through mammogram screening has been associated with increased survival rates for breast cancer patients. When cancer is diagnosed and treated at an early, localized stage, the chances of successful treatment and survival are generally higher.
- Identification of Abnormalities Before Symptoms Occur:
- Mammograms can detect abnormalities such as tumors or calcifications in the breast tissue before any symptoms, such as lumps or pain, become noticeable. This allows for prompt investigation and intervention.
- Screening for High-Risk Individuals:
- Women with an increased risk of developing breast cancer, such as those with a family history of the disease or certain genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2), can benefit from regular mammogram screening as a proactive measure.
- Guidance for Further Diagnostic Testing:
- If a mammogram shows an abnormality, it can serve as a guide for additional diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound or biopsy, to further evaluate the nature of the findings. This helps in confirming the diagnosis and planning appropriate treatment.
- Monitoring Changes Over Time:
- Regular mammogram screening provides a baseline for comparison in subsequent screenings. Monitoring changes in breast tissue over time allows healthcare providers to detect any new developments or changes that may indicate the presence of cancer.
- Reduction in Mortality Rates:
- Population-based screening programs with mammography have contributed to a reduction in breast cancer mortality rates. Early detection and timely treatment can be crucial in preventing the progression of the disease to an advanced and less treatable stage.
- Customized Screening Plans:
- Healthcare providers can develop personalized breast cancer screening plans based on factors such as a woman’s age, family history, and overall health. This allows for tailored screening recommendations to optimize benefits and minimize potential harms.
- Educational Opportunities:
- Mammogram screening provides an opportunity for healthcare providers to educate women about breast health, the importance of regular screenings, and risk factors for breast cancer. This can empower women to actively participate in their health and well-being.
According to the latest research, about 7 deaths out of 1,000 women who have mammograms every 2 years for 20 years are preventable. Getting mammograms at regular intervals can prevent a patient’s risk of dying from cancer.
There are many advantages to detecting breast cancer at an early stage. One of the major advantages is that it becomes possible to cure breast cancer without chemotherapy.
It has been noted that 98.99% of women will not develop breast cancer if cancer is not detected by periodic mammogram screens and other exams.
What is the Mammography test cost
Generally the cost of breast mammographi varies from one diagnostic center to another. Before you go to the testing center, inquire about breast mammography prices in a couple of places.
The cost of mammographi test in South Asia depends on the type of test being done. A routine breast scan can cost between a dollar. 19 more dollars. 25, while a digital mammogram can cost as much as $. 100. Regardless of the cost of mammograms, you should have regular self-examinations of your breasts.
Mammography Troubleshooting
Mammograms are complex medical imaging systems, and their diagnosis usually requires the expertise of trained professionals, such as radiologists, radiologic technologists, or biomedical engineers. However, I can provide you with some general troubleshooting steps that are commonly followed in case of problems with mammography machines. These steps are for informational purposes only and should not take the place of professional guidance. It is essential to consult a qualified technician or service provider for accurate troubleshooting and repair.
- Check power and connections: Make sure the mammography machine is properly connected to a power source and that all cables and connections are secure. Look for and replace any loose or damaged cables and connectors.
- Check display and controls: Check that the display screen and control panel are working properly. If there are error messages or abnormal indications, consult the machine’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for guidance on specific error codes or messages.
- Restart the system: Sometimes, technical problems can be resolved by restarting the mammography machine. Shut down the system, wait a few seconds, and then turn it back on.
- Quality Control Tests: Mammography machines undergo regular quality control tests to ensure optimum performance. If there are image quality issues, artifacts, or inconsistencies, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended quality control procedures or consult with the service provider.
- Image Acquisition and Processing: If there is a problem with image acquisition or processing, check patient position, compression pedals, and breast alignment. Make sure exposure parameters are set correctly, and image acquisition software is working properly.
- Maintenance and Service: Mammography machines require regular maintenance and service to ensure their proper functioning. Follow the recommended maintenance schedule and contact the manufacturer or an authorized service provider for routine maintenance or repair.
FAQ
What is the difference between mammography and tomosynthesis
Mammography and tomosynthesis are both imaging techniques used for breast screening and diagnosis, but they differ in their approach and the information they provide. Mammography is a well-established screening method for detecting breast abnormalities, including early signs of breast cancer. Tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography that provides three-dimensional images of the breast.
What is digital mammography
Digital mammography, also known as full-field digital mammography (FFDM), is an advanced imaging technique used for breast screening and diagnosis. It is an alternative to traditional film-screen mammography, offering several advantages.
What is 3d mammography
3D mammography, also known as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) or breast tomosynthesis, is an advanced imaging technique used for breast screening and diagnosis. It is an extension of digital mammography that provides three-dimensional images of the breast.
What is diagnostic mammography
Diagnostic mammography is a specialized imaging technique used to further evaluate breast abnormalities detected during a screening mammogram or to investigate specific breast concerns or symptoms. It is performed when there is a need for a more detailed assessment of a particular area or when additional imaging is necessary.






