What is ablation?
In a healthy human heart, the rhythm is steady and coordinated. It keeps on slowing down or speeding up as it adapts to the changes taking place in the body. Your heart rate affects how much blood and oxygen is circulating through your body.
It is commonly seen that some people develop abnormal cells in the heart that keep interrupting the electrical signals. In this the heart does not beat how it should, and the person experiences an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
Medicines recommended by the service provider can help control the abnormal tissue that causes the arrhythmia. However, they are not effective for everyone and can cause side effects and also do not address the underlying problem.
In the cardiac ablation procedure, the arrhythmia is corrected by treating the tissue with targeted energy. It restores normal function and eliminates symptoms.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
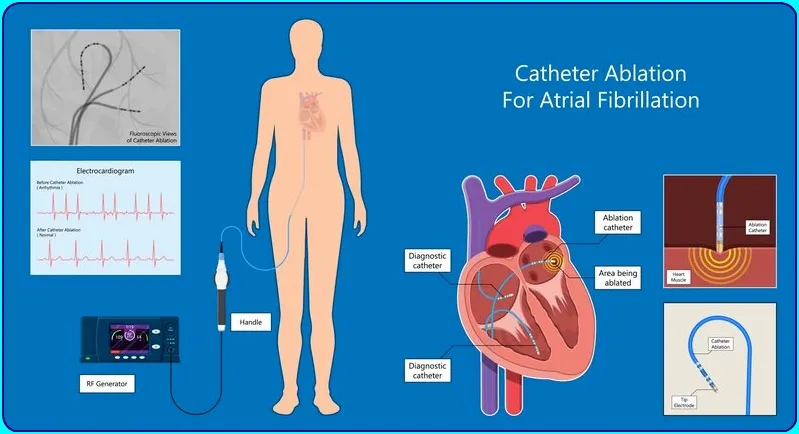
Thus we can tackle arrhythmias that are difficult to treat with drugs using a minimally invasive, drug-free approach.
Ablation uses a catheter (small tube) placed through a blood vessel into the heart and is also called catheter ablation.
Once the service provider has identified the tissue involved in the heart arrhythmia, he or she targets that area by heating or cooling. This creates tiny scars in your heart (ablation lines), which block arrhythmic electrical signals from passing through nerve pathways.
What is cardiac ablation?
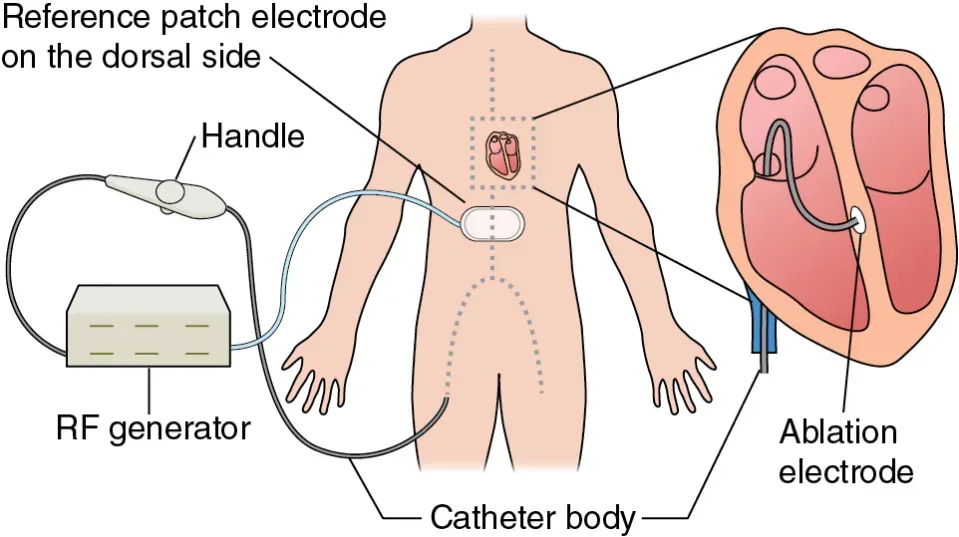
Cardiac ablation is an intensive procedure performed by an interventional cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in procedures for heart problems. This procedure involves threading a catheter (long flexible wire) through a blood vessel and into your heart. The cardiologist uses electrodes to deliver a safe electrical pulse to areas of your heart to treat irregular heartbeats.
Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive treatment for heart palpitations. A catheter is a thin flexible tube that is inserted through a blood vessel into your heart. Catheter ablation is a type of heart ablation procedure used to treat abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Ablation is a technique used by a heart specialist to strategically destroy abnormal tissue and restore proper function of your heart.
In this procedure, hot or cold energy is used to create scars in your heart tissue where the arrhythmia is occurring. And the scars in it help to block abnormal electrical impulses and prevent abnormal rhythms. Also scars only destroy the tissue associated with the faulty heart pattern. They don’t cause any residual pain or, let’s say, cause problems with your heart function.
When is cardiac ablation required?
Sometimes your heart beats too fast, too slowly, or unevenly. These heart rhythm problems are called arrhythmias and can be treated using cardiac ablation. Arrhythmias are very common in some people, especially in older adults and in people who have diseases that affect their hearts.
People who may see improvement with cardiac ablation include those who:
1) have an arrhythmia that does not respond to medication
2) suffer bad side effects of arrhythmia medicine
3) have a specific type of arrhythmia that responds well to cardiac ablation
4) are at higher risk for sudden cardiac arrest or other complications
Cardiac ablation is helpful for people with these specific types of arrhythmias.
1) AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT): Very fast heartbeat due to a short circuit in the heart.
2) Accessory Pathway: Rapid heartbeat due to abnormal electrical pathways connecting the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
3) Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: An irregular and rapid heartbeat that starts in the two upper chambers of the heart.
4) Ventricular tachycardia: a very rapid and dangerous rhythm that begins in the heart’s two lower chambers

What happens during cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is performed in a special room also known as an electrophysiology laboratory. The health team includes cardiologists, technicians, nurses and anesthesia providers. The process can usually take three to six hours to complete. It is performed under general anesthesia or under local anesthesia with sedation.
Before you start your anesthesia provider gives you medicine through an intravenous (IV) line that will make you sedated and cause you to fall asleep. And the device monitors your heart’s electrical activity.
The cardiologist cleans and numbs an area of skin on your arm, neck, or groin. Next, the cardiologist threads a series of catheters through a blood vessel into the heart. And they inject a special type of contrast dye to help you see areas of abnormal muscles in your heart. The cardiologist then uses a catheter with electrodes at the tip to direct a burst of radiofrequency energy. This electrical pulse destroys small portions of abnormal heart tissue to correct your irregular heartbeat.
What are the risks involved in cardiac ablation?
Risks usually include bleeding, pain, and infection at the catheter insertion site. More serious complications are rare, but can mainly include:
1) Forming blood clots.
2) Damage to your heart valves or arteries.
3) Fluid buildup around your heart.
4) Having a heart attack.
5) Pericarditis, or inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart.

What happens after cardiac ablation?
You may feel tired and experience some slight discomfort during the first 48 hours after the test. Follow your doctor’s instructions about wound care, medications, physical activity, and follow-up appointments. Have periodic electrocardiograms and review rhythm strips to monitor heart rhythm.
Some people may have short episodes of irregular heartbeat even after cardiac ablation. This is a normal reaction as the tissue heals, and fades away over time.
The cardiologist will tell you if you need any other procedures, including pacemaker implantation, especially those used to treat complex heart rhythm problems.
What conditions does Catheter Ablation treat?
Catheter ablation treats all types of rapid heart arrhythmias. The cardiologist may suggest catheter ablation if you have an abnormal heart rhythm that is not treated with medication.
The main types of arrhythmias that can be treated with catheter ablation include:
1) Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and atrial flutter:- AFib and atrial flutter cause the upper chambers of your heart to beat irregularly and ineffectively. It quiveres instead of shrinks. This lack of contraction keeps blood from pumping through your heart properly. AFib can cause clots that increase your risk of stroke as blood stagnates in your left atrium.
2) Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT):- People with SVT may experience episodes of fast, irregular heartbeat (up to 310 beats per minute). In this the heart can still pump blood normally, but repeated, or long-lasting, SVT attacks can damage your heart.
3) Ventricular tachycardia (VT):- The lower chambers, called ventricles, begin to beat rapidly and freely, a potentially very dangerous arrhythmia that sometimes leads to cardiac arrest.
If you are at low risk, you may have a cardiologist recommend catheter ablation:
1) Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib):- An ineffective and irregular heartbeat originating in the ventricles (lower heart chambers).
2) Sudden cardiac arrest:- When your heart stops without warning.

Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports
What are the types of catheter ablation procedures?
Catheter ablation uses hot or cold energy to scar the heart tissue. The cardiologist chooses the method he is most comfortable with and that best suits your situation. You will receive sedation or possibly general anesthesia during the procedure and may not feel any extremities hot or cold.
Types of catheter ablation include:
1) Radiofrequency ablation:- Radiofrequency delivers heat energy to the heart tissue.
2) Cryoablation:- Cryoablation uses cold energy to freeze and scar the heart tissue.
How much does it cost to get an ablation?
This procedure typically costs an average of $4,200 – $11,600, a cost that varies by city. You can also use health insurance for all this.
FAQ
What is cardiac ablation procedure?
Cardiac ablation is a medical procedure used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias. During the procedure, a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) is guided through blood vessels to the heart. The catheter delivers energy, such as radiofrequency or cryotherapy, to destroy or ablate the abnormal tissue causing the arrhythmia. By eliminating or disrupting the abnormal electrical pathways, cardiac ablation can restore a normal heart rhythm. It is typically performed by electrophysiologists, specialists in heart rhythm disorders.
How serious is heart ablation surgery?
Heart ablation surgery is generally considered a safe and effective procedure. However, like any surgical procedure, it does carry certain risks and potential complications. The specific risks can vary depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the type of arrhythmia being treated, and the specific technique used during the ablation.
Is a pacemaker better than ablation?
Pacemakers and ablation serve different purposes and are used to treat different conditions related to heart rhythm disorders. The choice between a pacemaker and ablation depends on the specific diagnosis and individual circumstances. Let’s look at their respective roles:
Pacemaker: A pacemaker is a device implanted under the skin that helps regulate the heart’s electrical activity. It is typically used when there is a problem with the heart’s natural pacemaker (the sinoatrial node) or when there are issues with the electrical signals traveling through the heart. Pacemakers are mainly used to treat bradycardia, a condition characterized by a slow heart rate.
Ablation: Cardiac ablation is a procedure that aims to eliminate or disrupt abnormal electrical pathways in the heart causing arrhythmias. It is primarily used to treat certain types of tachycardias, such as atrial fibrillation or supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). By targeting and destroying the abnormal tissue, ablation can restore a normal heart rhythm.
What are the side effects of an ablation?
Cardiac ablation is generally considered a safe procedure, but there can be potential side effects or complications. These can vary depending on factors such as the type of ablation being performed, the specific arrhythmia being treated, and individual patient characteristics. Here are some possible side effects or complications:
Bleeding or bruising: Some bruising or bleeding may occur at the catheter insertion site. This is usually minor but can occasionally require intervention.
Infection: Infection is a possible complication, although it is relatively rare. The risk can be minimized by following proper sterile techniques during the procedure.
Blood vessel damage: During catheter insertion, there is a small risk of damaging a blood vessel. This can cause bleeding or necessitate further intervention.
Arrhythmias: Cardiac ablation aims to correct arrhythmias, but it can also cause new arrhythmias to develop. These are usually temporary and resolve on their own, but in rare cases, they may require additional treatment.
Damage to heart structures: In rare instances, the ablation procedure can unintentionally damage the heart’s normal structures. This may require further intervention or surgery to repair.
Blood clots: There is a small risk of blood clot formation during or after the procedure. Anticoagulant medications are typically used to minimize this risk.
Phrenic nerve injury: In some cases, the phrenic nerve, which controls the diaphragm, can be affected during ablation near the heart’s chambers. This can result in temporary or permanent diaphragm weakness or paralysis.
Perforation or tamponade: In rare cases, the catheter can perforate the heart or cause cardiac tamponade, which is the accumulation of fluid around the heart. These are serious complications requiring immediate medical attention.
It’s important to note that serious complications from cardiac ablation are relatively rare, and the procedure is generally considered safe and effective. The specific risks and potential complications should be discussed with your healthcare provider, who can provide more personalized information based on your individual circumstances.
How much does heart ablation procedure cost?
The cost of a heart ablation procedure can vary significantly depending on various factors, including:
Geographic location
Healthcare provider
Type of facility
Specific procedure
Insurance coverage
For example, one study found the median patient cost for catheter ablation was $32,756.
hat if cardiac ablation doesn’t work
If cardiac ablation does not provide the desired outcome or fails to resolve the heart rhythm disorder, there are several alternative options that can be considered:
Medications: If ablation is not successful, medications may be prescribed to manage and control the heart rhythm disorder. Anti-arrhythmic drugs can help regulate the heart’s electrical activity and control the symptoms associated with the arrhythmia. Different medications can be tried or the dosage adjusted to achieve optimal results.
Implantable devices: Depending on the specific condition, implantable devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be recommended. These devices can help regulate the heart’s electrical activity or provide a shock to restore a normal rhythm if a life-threatening arrhythmia occurs.
Catheter-based techniques: If traditional ablation methods are not successful, alternative catheter-based techniques may be explored. These can include different energy sources or mapping techniques that can provide more precise targeting of the abnormal tissue causing the arrhythmia.
Surgical procedures: In certain cases, open-heart surgical procedures may be considered as an alternative. These can involve removing or modifying the problematic areas of the heart that are causing the arrhythmia.
Hybrid procedures: Hybrid procedures combine both catheter-based techniques and surgical approaches. They involve a collaboration between electrophysiologists and cardiac surgeons to address complex or difficult-to-treat arrhythmias.
Ongoing management and lifestyle modifications: If other treatment options are not successful or not feasible, the focus may shift to ongoing monitoring, symptom management, and lifestyle modifications. This can involve regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and managing risk factors such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
It’s crucial to consult with a cardiac electrophysiologist or a specialized heart rhythm specialist to discuss the options available based on your specific situation. They can evaluate the cause of treatment failure and recommend the most appropriate next steps for managing your heart rhythm disorder.
how long does a cardiac ablation take
The duration of a cardiac ablation procedure can vary depending on several factors, including the type of arrhythmia being treated, the complexity of the case, the techniques used, and the individual patient’s anatomy. On average, a cardiac ablation procedure typically takes around 2 to 4 hours. However, it can sometimes take longer, especially for complex cases or if multiple ablations are being performed.
where is the catheter inserted for cardiac ablation
During a cardiac ablation procedure, the catheter is inserted into the body through blood vessels. The most common site of catheter insertion is the groin area, specifically the femoral vein or artery. The healthcare provider makes a small incision near the groin and inserts a sheath, a short hollow tube, into the blood vessel. Through this sheath, one or more catheters are threaded up to the heart.
why am i so tired after my cardiac ablation
Feeling tired or fatigued after a cardiac ablation procedure is not uncommon and can be attributed to several factors:
Anesthesia: The use of anesthesia during the procedure can leave you feeling groggy or tired as its effects wear off. The type and duration of anesthesia can vary, and some individuals may experience a longer recovery period.
Physical stress: Cardiac ablation is an invasive procedure that puts stress on the body. This can lead to fatigue as your body recovers from the procedure.
Medications: You may be prescribed medications following the ablation procedure, such as pain medications or anti-arrhythmic drugs. Some medications can cause drowsiness or fatigue as side effects.
Sleep disruption: The procedure itself and the recovery period can disrupt your normal sleep patterns. Changes in sleep quality or duration can contribute to feelings of fatigue.
Emotional and psychological factors: Going through a medical procedure can be emotionally and psychologically draining. Anxiety, stress, or emotional exhaustion can manifest as fatigue.
It’s important to note that post-procedure fatigue is usually temporary and should improve as your body heals. However, if fatigue persists or worsens over time, it’s recommended to discuss it with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your specific situation, consider other potential causes, and provide appropriate guidance or additional recommendations to address your fatigue.