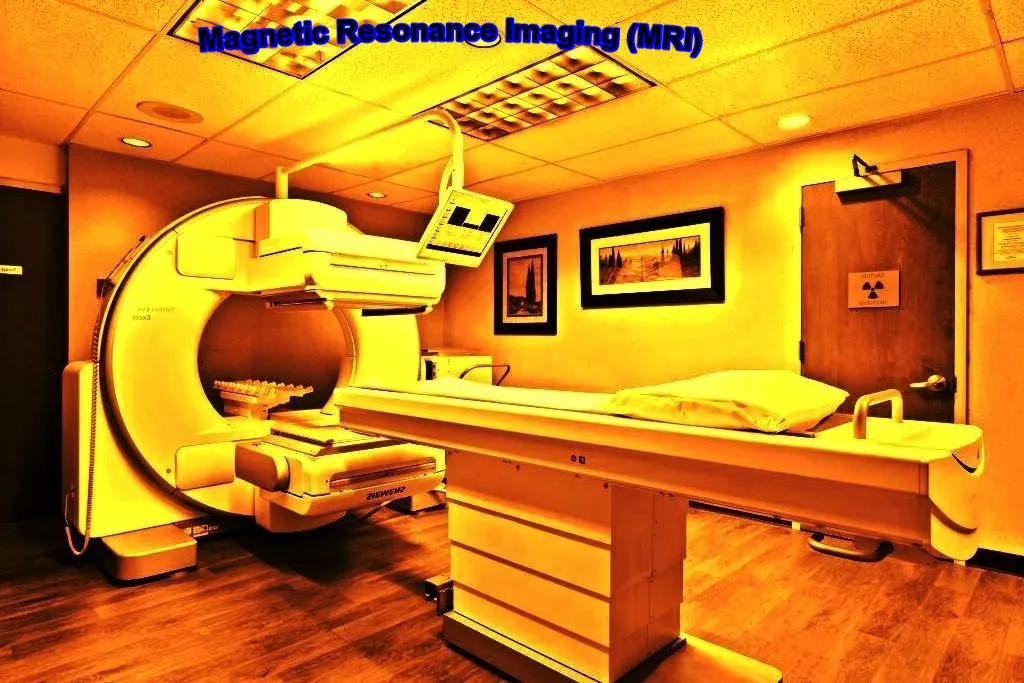
What is MRI machine
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique for imaging various sections of the human body, particularly soft tissue, as opposed to X-rays, which typically take images of the body’s hard components.
Unlike X-rays, which can only record pictures in vertical planes, MRI allows the physician to photograph their patient from any angle.
What is the working principle of MRI machine
MRI pictures are basically spectral images of hydrogen atom distribution in bodily fluids. To begin, the MR scanner creates a strong magnetic field on the Z axis, which transports hydrogen atoms down the magnetization axis.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:- Sports

This can be thought of as protons moving at the Larmer frequency. This is followed by a 90° RF pulse that moves the hydrogen atoms to the X-Y plane. The MRI scanner captures the image during this stage. The protons move again and align themselves on the Z axis.
Therefore to increase the time period of the atoms along the X-Y plane, a 180° spin echo pulse is applied to flip the atoms to the negative X-Y plane. Thus the time of stay in the X-Y plane is doubled.
The motion of atoms differs due to T1 and T2 effects so the differential I preposition develops the motion spectrum. The higher the speed, the brighter the image, the lower the speed, the darker the image.
The distribution spectra of fat are small but the distribution spectra of water are broad so the contrast in the image is seen depending on the type of tissue present in different tissues of the body.
What is the difference between CT Scan and MRI
CT differs from MRI in working principle, one has X-radiation and the other has magnetization technology.
CT scans have more side effects because excessive exposure to radiation can cause changes in tissue genetics that MRI does not.
Whereas MRI is costlier than city scan.
A CT scan is generally good for larger areas, while an MRI scan produces a better overall image of the tissue under investigation.
Digital radiography (DR) is an advanced form of x-ray inspection which produces a digital radiographic image instantly on a computer. This technique uses x-ray sensitive plates to capture data during object examination, which is immediately transfer to a computer without the use of an intermediate cassette.
How to work MRI machine?
MRI machines are made by employing powerful magnets that generate a strong magnetic field that forces protons in the body to align with that field.
When a radiofrequency current is pulsed through the patient, the protons begin to get excited, and move out of equilibrium with this pressure against the pull of the magnetic field.

When the radiofrequency field is turned off, MRI sensors are able to detect the energy released as the protons re-align with the magnetic field.
The time it takes for the proton to re-align with the magnetic field, as well as the amount of energy released, varies depending on the environment and the chemical nature of the molecules.
Physicians are able to differentiate between different types of tissues based on these magnetic properties.
To obtain an MRI image the patient is placed inside a large magnet and must remain very still during the imaging process in order not to blur the image.
Contrast agents often containing the element gadolinium are given intravenously to a patient before or during an MRI to increase the movement of protons with a magnetic field. The faster the protons become real, the brighter the image becomes.
What is MRI machine used for?
MRI machines are particularly well suited to image non-bony parts of the body or soft tissues. It differs from computed tomography (CT) in that it does not use harmful ionizing radiation from X-rays.
The brain, spinal cord, and nerves as well as muscles, ligaments and tendons are seen more clearly with MRI than with regular X-rays and CT. This is why MRI is often used to treat knee and shoulder injuries. is done for the image.
MRI scanners in the brain can differentiate between white matter and gray matter and can also be used to diagnose aneurysms and tumors.
Because MRI does not use X-rays or other radiation, it is the imaging method of choice when persistent imaging is needed for diagnosis or therapy, especially in the brain.
One type of specialized MRI is functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). It is used to observe brain structures and determine which areas of the brain are “active” during various cognitive tasks that consume the most oxygen.
It is used to advance the understanding of brain organization and to assess neurological status and neurosurgical risk. Provides good potential reports.
How long does an MRI scan take?
The exam usually takes 35 to 50 minutes to complete, depending on the type of exam and the equipment used. The healthcare provider will be able to give a more accurate time frame based on the specific reason for your scan.
What are the risks of an MRI machine?
The MRI machine does not emit the ionizing radiation found in X-rays and CT imaging, but it does employ strong magnetic fields.
The magnetic field extends beyond the machine and exerts a powerful force on iron objects, some steels and other magnetic objects. Patients should inform physicians about any type of therapy or transplant before MR scan.
People with implants, especially those containing iron, – pacemakers, vagus nerve stimulators, implantable cardioverters – defibrillators, loop recorders, insulin pumps, cochlear implants, deep brain stimulators, and capsules from capsule endoscopy, etc.
Access to an MRI machine if implantation has occurred Shouldn’t.
Noise – Loud sounds known as clicking and beeping, as well as sound intensities of up to 120 decibels in some MR scanners, may require ear protection.
Nerve stimulation– Sometimes MRI shows a twitching sensation from rapidly switched areas.
Contrast agents– Patients with kidney failure who require dialysis or who are being treated on dialysis may be at risk for a rare but serious disease called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis,
which may occur with certain gadolinium-containing agents such as gadodiamide and others. may be associated with use.

Dialysis patients receive the gadolinium agent only when necessary, and that agent should be removed from the body as soon as possible after the scan. If possible, then dialysis should be done.
Pregnancy – no effect on the fetus has been shown, MRI scans to be avoided as a precaution, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy when fetal organs are forming and contrast agents may enter the fetal bloodstream, if ingested can. ,
Claustrophobia – Patients with mild claustrophobia may find it difficult to tolerate long scan times inside the machine.
Visualization techniques, sedation and anesthesia, along with familiarity with the machine and procedure, provide mechanisms for patients to relieve their discomfort.
What is the cost of MRI machine?
The average price for a new MRI machine for all manufacturers ranges from $150,000 to $650,000 for the machine, plus additional fees for servicing, logistics, and some options and features, which vary between manufacturer and model. Buying used or refurbished can significantly reduce this initial cost.
What is the cost of MRI test
People in clinical centers spend between $65 and $75 with additional fees if patients want a more in-depth study of the organ.
Advantages of DR system
- Similar to digital photography.
- It does not require darkroom procedure and cassette reading.
- It reduces X-ray printing time.
- X-ray directly converted into an electronic signal, convert into digital values, and into images.
Basic components of DR system
1. A digital image receptor
2. A digital image processing unit
3. Image and data storage devices
4. Interface to a patient information system
5. Communications network
6. A display device with viewer operated controls.

Digital Receptor
The digital receptor is the device that intercepts the x-ray beam after it has passed through the patient’s body and produces an image in digital form, that is, a matrix of pixels, each with a numerical value.
This replaces the cassette containing intensifying screens and film that is use in non-digital, film-screen radiography.
Image Management System
Image management is a function perform by the computer system associate with the digital radiography process.
These functions consist of controlling the movement of the images among the other components and associating other data and information with the images.
Patient Information System
The Patient Information System, perhaps known as the Radiology Information System (RIS), is an adjunct to the basic digital radiography system. Through the interface, information such as patient ID, scheduling, actual procedures perform etc.
Imaging Processing
One of the major advantages of digital radiography is the ability to process the images after they are recorde. Various forms of digital processing can use to change the characteristics of digital images. For digital radiographs, the ability to change and optimize the contrast is of great value.
It is also possible to use digital processing to enhance the visibility of detail in some radiographs. The various processing methods are explore in much more detail in another module.
Digital Image Storage
Digital radiographs, and other digital medical images, are store as digital data.
Communications Network
Another advantage of digital images is the ability to transfer them from one location to another very rapidly.
This can be:
Within the imaging facility to the storage and display devices and To other locations (Teleradiology) Anywhere in the world. (by means of the internet)
Digital Image Display and Display Control
Compared to radiographs recorded and displayed on film, i.e. “softcopy”, there are advantages of “softcopy” displays.
Basic components of Radiography
- X-ray tube
- X-ray detector
- Collimator
- HV generator
- Filters
- Console computer
X-ray tube
- Includes cathode, anode, and casing.
- Cathode filament is supplies with 20-150 KV.
- X-ray produced by mainly two method electron ejection and electron deceleration.
- Electron ejection (Characteristic X-ray radiation): Fast-moving electrons hit electrons in the innermost shell, hence electron vacancy is create, to occupy this vacancy by an electron from another shell by emitting X-ray radiation.
- Electron deceleration (Bremsstrahlung radiation): When fast-moving electrons come to an anode, anode atoms look as Positive nucleus and negative electrons thus it moves any region emitting X-ray radiation.
- Heating curve: time taken to achieve particular MA and KV.
- Cooling curve: time is taken to cool the X-ray tube.
- Energy at x-ray tube= Kv* MA*.
- No of electrons in X-ray depends current, a voltage which improves the intensity of x-ray beam.
H V generator
- Used for giving supply to the X-ray tube.
- Voltages ranges.
- This mainly includes single phase or three phases.
- Supply specification mainly represented by Peak kilovoltage (Kvp).
- H V: Transformer Step up the input voltage.
- Rectifier: It converts High voltage Ac supply into Dc supply.
- Chopper: Increases the frequencies up to 200KHZ High-frequency supply improves the maximum (Kvp) for exposure, it gives better image intensity and improves the Tube lifetime.
Image receptor
- It absorbs attenuated X-ray radiation into image form.
- It includes image receptor permanent cassette.
- It includes Matrix array of Semiconductor (Thin-film transistor) devices normally in off position.
- During Expose it Changed to ON position.
- Signal from each semiconductor amplified by Preamplifier.
- Amplified signals given to ADC converter which converts the analog signal into digital signal then given to the digital processor.
Mainly it includes two types
a. Direct receptor:
Made up of amorphous selenium It directly converts Input x-ray into electric signals, Then Analog to Digital converter, this digital signal is process by the digital processor
b. Indirect receptor:
Made up of Gd2o2S/CSI: It converts input X-ray into light signals then it is given to photodetector, it converts light into an electric signal. Then analog to digital converter converts the electric signal into a digital signal and is process by a digital processor.
COLLIMATOR & GRIDS
- Present Between X-ray tube and patient.
- Collimator light is expose to a patient before x-ray exposure.
- It provides proper positioning of an X-ray tube.
- Grids are lead strips inserte between patient and film cassette.
- It is used to reduce the contrast due to scattered radiation Basic principle
When a monochromatic light source passes through a medium, attenuation of light is directly proportional to the concentration of substance present in the solution
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
When X-ray radiation from an X-ray tube passed through the body, then it falls to the X-ray detector. The detector converts the X-ray into an electrical signal and then it is digitize by A-D Converter.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a MRI machine used for?

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides three-dimensional anatomical pictures. It is frequently employed in illness detection, diagnosis, and therapy monitoring.
What is difference between CT scan and MRI?

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides three-dimensional anatomical pictures. It is frequently employed in illness detection, diagnosis, and therapy monitoring.
What is an MRI How is it done?
During an MRI, you typically lie on a table that moves through a tunnel in the center of the MRI scanner. To create signals from the body, the scanner employs high magnetic fields and radio waves. These are detected by a radio antenna and processed by a computer to provide detailed images.
What are the side effects of MRI scan?

Most people are unaffected by MRI contrast. Individuals with renal problems and pregnant women, on the other hand, should consult their doctor before undergoing an MRI with contrast. Contrast material side effects are typically modest and may include a rash, nausea, and vomiting.
Is MRI good for body?

The MRI scan is a completely risk-free treatment. Metal objects (such as jewellery) worn during the scan may cause damage on rare occasions. Internal metal devices, such as a cardiac pacemaker, may be damaged by the MRI scanner’s intense magnetic field.
What is the cost of MRI machine?

The price of a 1.5 tesla MRI scanner ranges from 30 lakh to 4 crore. The 1.5T MRI machine is a closed MRI that provides high-quality imaging.
Is MRI better than CT?

When compared to a CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging gives sharper pictures. When clinicians need a picture of soft tissues, an MRI is preferable to x-rays or CT scans. When compared to CT scans, MRIs can produce more accurate images of organs and soft tissues, such as damaged ligaments and herniated discs.
Which scan is best for brain?

MRI gives very accurate and comprehensive pictures of the human brain, allowing healthcare experts to analyze its structure and diagnose any anomalies. MRI does not employ ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays or CT scans, making it a safer alternative for recurrent imaging.
Why are MRIs so expensive?

The entire cost of an MRI scan comprises a technical charge, a professional fee, and a facility fee. Furthermore, the technology necessary for an MRI may cost between $150,000 and $3 million, and a tailored room must be developed to eliminate interference from other medical imaging procedures.
How long is a MRI take?

How long does an MRI examination take? A single scan might take seconds or up to 8 minutes. During brief scans, you may be requested to hold your breath. The overall scan time ranges from 15 to 90 minutes, depending on the size of the area being scanned and the number of photos required.





