Electroencephalogram EEG
Article About:-Sports
How to work electroencephalogram
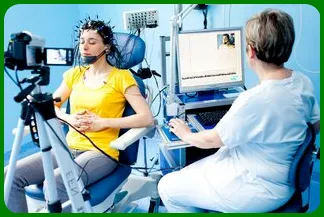
An EEG, also called a brain wave test, is a procedure that measures electrical activity in the brain. The doctor will place sensors on your head and ask you to relax. The sensors are connected to a machine that records your brain waves. The test is painless and usually takes about an hour.
How are EEG signals generated?
EEG signals are generated by the brain’s neurons. When a neuron is active, it produces a small electrical signal. This signal can spread to other neurons and cause them to become active. The electrical activity of many neurons can create an EEG signal.
EEG signals are usually very weak, so they must be amplified before they can be recorded. The amplifiers used for EEG are very sensitive, so they can pick up even the smallest EEG signals.
Once the EEG signals have been recorded, they can be analyzed to look for patterns of brain activity. These patterns can provide information about what the person is thinking or feeling.
How long does a EEG test take?
An EEG test usually takes around 30 to 60 minutes.
What EEG means?
EEG, or electroencephalography, is a test that measures electrical activity in your brain. This test can help your doctor diagnose seizures or other problems with your nervous system.
During an EEG, sensors called electrodes are placed on your scalp. These sensors pick up the electrical signals from your brain and send them to a computer. The computer displays these signals as wavy lines.

EEG is a painless test, and it only takes a few minutes. You will probably be able to go home after the test is done.
If you have any questions about EEG, be sure to ask your doctor.
What does EEG test for?
An EEG, or electroencephalography, is a test that measures electrical activity in the brain. This test can be used to diagnose epilepsy or other brain disorders.
The test is usually done by a neurologist, and it usually takes about an hour. EEG can also be used to monitor brain activity during surgery.
EEG working principle
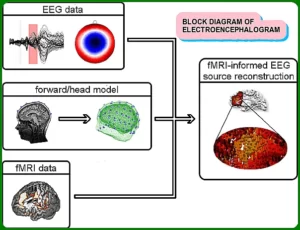
Electroencephalography, or EEG, is a method of recording electrical activity from the brain. This activity can be used to diagnose and treat various neurological conditions.
EEG works by placing electrodes on the scalp. These electrodes pick up tiny changes in electrical voltage from the brain. The changes are then amplified and recorded on a computer.
EEG is a safe and painless procedure that can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including:
1.) Epilepsy
2.) Sleep disorders
3.) Head injuries
4.) Strokes

FAQ
What does an electroencephalogram measure

An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive neurophysiological test that measures and records the electrical activity of the brain. It detects and records the electrical impulses generated by the neurons (brain cells) in the form of brain waves.
how does an electroencephalogram work

An electroencephalogram (EEG) works by detecting and recording the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how an EEG typically works:
Preparation.
Electrode Placement.
Signal Detection.
Signal Recording.
Interpretation.what does an electroencephalogram (eeg) measure?

The EEG measures the brain’s electrical activity by capturing the voltage fluctuations produced by the synchronized firing of neurons. These electrical signals are typically in the range of microvolts and are represented as brain waves on the EEG recording.
Delta Waves (0.5-4 Hz).
Theta Waves (4-8 Hz)..
Alpha Waves (8-13 Hz)..
Beta Waves (13-30 Hz).
Gamma Waves (30-100 Hz.which code represents electroencephalogram, cerebral death evaluation only?

The specific code used to represent an electroencephalogram (EEG) for cerebral death evaluation may vary depending on the coding system used. Here are the relevant codes for different coding systems:
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code.
International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code.