Electron Microscope Images
This essay will go over the various image formats generated by electron microscopy and how they differ from images captured using a conventional microscope. We’ll also look at common uses for this method and the kinds of images that may be created from electron microscope images. The topic of electron microscope images will be covered in this essay.
What is an electron Microscope images?
An electron microscope images is an image created using an electron microscope. This type of microscope uses a beam of electrons to form an image of a sample. The electrons are passed through a series of magnets that focus the beam onto the sample. The resulting image is then magnified and displayed on a screen.
What is the working principle of electron microscope?
Electron microscopes use a beam of electrons instead of visible light to achieve much higher resolution than light microscopes. There are two main types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscopes (TEM) and scanning electron microscopes (SEM). Here’s a brief overview of their working principles:
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM):
- Electron Source: A TEM uses an electron gun to produce a beam of electrons.
- Condenser Lens: The electron beam passes through a condenser lens system, which focuses and shapes the beam.
- Specimen: The specimen, typically a thin section of the sample, is placed in the path of the electron beam.
- Transmission: Electrons that pass through the specimen are transmitted and collected on the other side.
- Objective Lens: The objective lens focuses the transmitted electrons to produce an image.
- Projector Lens: Finally, a projector lens magnifies the image onto a screen or a camera.
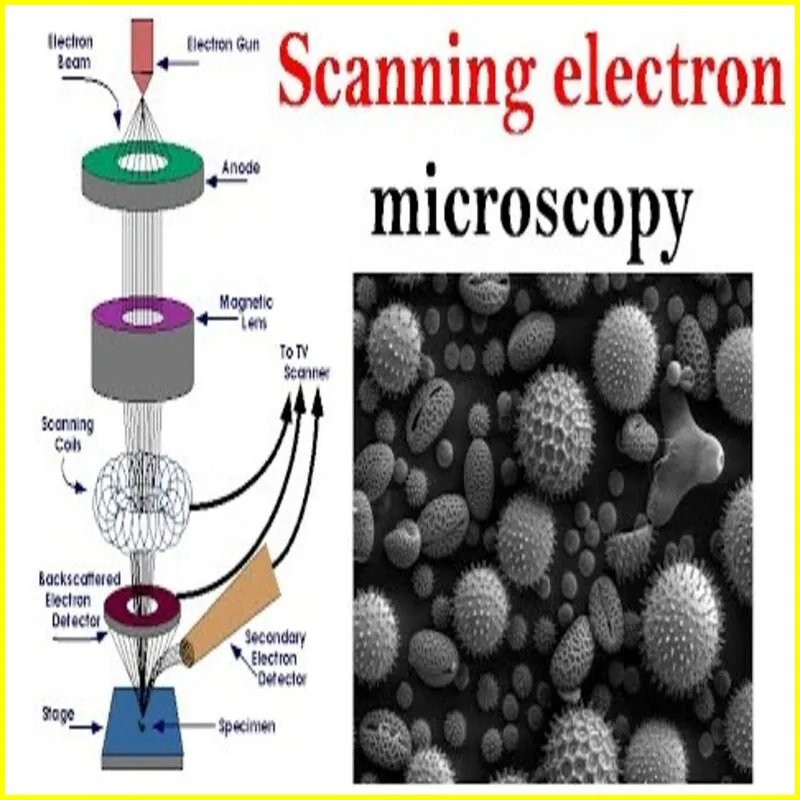
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM):
- Electron Source: An SEM also uses an electron gun to generate a beam of electrons.
- Condenser Lens: The electron beam is focused and directed toward the specimen.
- Specimen: The specimen is coated with a thin layer of conductive material to enhance electron interaction.
- Scanning Coils: The electron beam is scanned across the surface of the specimen in a raster pattern.
- Secondary Electrons: When the electron beam interacts with the specimen, it causes the emission of secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, and other signals.
- Detectors: Detectors capture these signals, and the information is used to create a detailed three-dimensional surface image of the specimen.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Tech
Article About:-Sports

How does an Electron Microscope Work?
An electron microscope uses a beam of electrons to produce an image of a sample. The electrons interact with the atoms in the sample, producing various signals that can be used to image.
There are two main types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). TEMs use a beam of electrons that passes through a very thin sample to produce an image. SEMs use a beam of electrons scanned over the surface of a sample to produce an image.
TEM is typically used to study small, delicate specimens, while SEM is better suited to study larger, more robust specimens. Both types of microscopes can produce very high resolution images, making them essential tools for scientific research.
Examples of Electron Microscopes
An electron microscope or electron microscope images is a type of microscope that uses electrons to form an image. There are two main types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM).
TEM creates an image by passing electrons through a sample. The electrons interact with the atoms in the sample, and this interaction produces a signal that is passed to a detector. SEM creates an image by scanning a focused beam of electrons across the surface of a sample. As the beam passes over the sample, it interacts with atoms on the surface of the sample, and this interaction produces a signal that is passed to a detector.
Both TEM and SEM can produce images with resolutions that are much higher than those of light microscopy. For example, TEMs can typically resolve features that are less than 0.1 nanometer in size, while SEMs can typically resolve features that are less than 1 nanometer in size.
What is the benefit of Electron Microscopes?
An electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. Electron microscopes have much higher resolutions than optical microscopes and can be used to observe objects on the nanometer scale.
There are two main types of electron microscopes: transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). TEM uses an electron beam that is transmitted through a thin sample to produce an image, while SEM uses an electron beam that is scanned across the surface of a sample to produce an image.
The major advantage of electron microscopes as compared to optical microscopes is their higher resolution. This allows them to be used to observe features that are too small to be seen with an optical microscope.
Another advantage of electron microscopes is that they can be used to study samples in a vacuum. This is important because many materials will degrade or change in structure when exposed to air or water. By studying samples in a vacuum, scientists can avoid these problems and obtain accurate results.
How to View an Electron Microscope Image
To view an electron microscope image, you will need a special type of microscope that is designed for this purpose. There are two main types of electron microscopes – transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). TEMs work by firing a beam of electrons through a very thin sample, while SEMs work by scanning the surface of a sample with a focused beam of electrons.
When compared to pictures observed with a light microscope, both varieties of electron microscopes create images that are magnified hundreds of times. Moreover, compared to images created by a light microscope, those generated by an electron microscope are often crisper and more detailed.
The easiest approach to examine an electron microscope image is to locate an internet resource that offers this kind of image. Though they are less prevalent, you could also come across certain books and publications that feature these kinds of photos. Once you have a picture, you may utilize it to study more about the electron microscope’s characteristics and how to understand the data it offers. pictures of electron microscopes, pictures of electron microscopes, pictures of electron microscopes
FAQ
Are electron microscope images real?

The image below on the right is the real image taken by a transmission electron microscope. You can see the scale bar (100 nm) below with a magnification 150,000x. In addition, the EM images are black and white. Therefore, the right image is the real image via an electron microscope.
What is electron microscopic images?
Electron microscopy (EM) is a technique for obtaining high resolution images of biological and non-biological specimens. It is used in biomedical research to investigate the detailed structure of tissues, cells, organelles and macromolecular complexes.
Can any microscope see electrons?
No, you can’t see an atom the way we’re used to “seeing” things – that is, using our eyes’ ability to perceive light. An atom is simply too small to deflect visible light waves, which means it won’t show up under even the most powerful light-focusing microscopes, Oncel said.
What can electron microscopes see?
Some electron microscopes can detect objects that are approximately one-twentieth of a nanometre (10-9 m) in size – they can be used to visualise objects as small as viruses, molecules or even individual atoms.
Can we see DNA under electron microscope?

Electron microscopes, too, can see DNA in cells, and DNA sequencers can determine the A’s, T’s, C’s, and G’s (nucleotides) it’s made of.
Can we see an electron with our eyes?

The sub-atomic particles of an atom are not visible. Hence, we cannot see an electron.
Is there a photo of electron?

Capturing an image of an electron in motion could have considerable impacts in fields like technology, medicine and beyond. Nobody has ever photographed an electron in motion. Mohammed Hassan, University of Arizona assistant professor of physics and optical sciences, wants to be the first.
What is the smallest thing we can see?

Experts believe that the naked eye — a normal eye with regular vision and unaided by any other tools — can see objects as small as about 0.1 millimeters.
What is electron microscope and its parts?
Microscope (TEM)
The glass lenses of an electron microscope are replaced by magnetic lenses, the light source by an electron source (a heated tungsten filament in vacuum), and the projection screen by a fluorescent screen that glows when electrons strike it.
What is the full name of the electron microscope?
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), in which quick electrons pass through a thin material, is another name for an electron microscope. TEM using a scanned electron probe is comparable to scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). STEM is comparable to the scanning electron microscope (SEM), however SEM uses thick materials.





