What is compound light microscope labeled
Have you always wanted to use a labeled compound light microscope to investigate the microscopic world but were unclear about how to use one? So that you can begin your exploration of the microscopic world equipped with a compound light microscope, we shall dissect every component of a compound light microscope and elucidate its purposes in this post.
What is a compound microscope?
A compound light microscope is a kind of light microscope that enlarges an object by using two or more lenses. The objective lens, which is the first lens, is placed close to the thing being observed. The eyepiece, a second lens, is situated close to the viewer’s eye.
Compound microscopes are frequently used to observe microscopic objects, including germs or cells. They are also used to see items, including tiny insects, that are hard to see with the unaided eye.
Different magnification levels can be achieved with compound microscopes by adjusting them. The power of the objective lens and eyepiece determines the magnification level.
Article About:- Health & fitness
Article About:- Medical Technology
Article About:-Sports

The function of parts of the microscope
Magnification of the image is the purpose of the labeled compound light microscope or eyepiece. The lens that is closest to your eye is the ocular lens. This aids in concentrating on the sample. The lenses beneath the stage are called objective lenses. They serve to increase the sample size even more. Slides should be placed on the stage. When you try to focus on the slide, the Stage Clip holds it in place so it doesn’t move. Typically, an electric bulb shining from underneath the stage serves as the light source. The sample is illuminated from below by it.
The lens that you use to see the specimen is called an eyepiece. Typically, ocular lenses have a 10x magnification power.
The three objective lenses are housed in the nosepiece, and they can all be adjusted to change their positions along the light path. The magnification of these objectives ranges from 4x to 40x.
The slide containing the material is positioned on the stage. It centers the specimen in the field of view by adjusting the X-Y coordinates and includes a stage clip to hold the slide in place. A light source, which could be an LED, halogen, or incandescent lamp, is located beneath the stage.
In addition to supporting the body of the microscope, the arm gives you a place to rest your hands while using the controls.
The coarse focus knob and the fine focus knob, two mechanical parts that regulate focus, are housed in the base, which also gives the microscope stability.
Pros and cons of a microscope
The compound light microscope labeled is a powerful instrument that can be used to view very small objects. However, there are some drawbacks to using a microscope.
One disadvantage of using a microscope is that it can be difficult to keep an object in focus. This is because the object is magnified, and the slightest movement can cause it to go out of focus. Furthermore, microscopes can be expensive, and they require proper care and maintenance.
Another disadvantage of using microscopes is that they can be dangerous if not used properly. For example, if you look at the Sun through a microscope, you can permanently damage your vision.
Despite these drawbacks, microscopes are still useful tools. They allow us to see things we might not be able to see otherwise, and can be used for both scientific research and medical applications.
Alternatives to microscopes
There are many different types of microscopes, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. Some microscopes are better for certain tasks than others. For example, scanning electron microscopes are better at observing the surface of objects than compound light microscopes labeled.
If you need to see objects in great detail, you may need to use a more powerful microscope such as an atomic force microscope or a confocal microscope. However, these microscopes are very expensive and may not be available to everyone.
There are also some alternative methods of microscopy that can be used to view objects. One method is fluorescence imaging, which can be used to observe fluorescent molecules. Another method is phase contrast imaging, which can be used to visualize transparent objects.
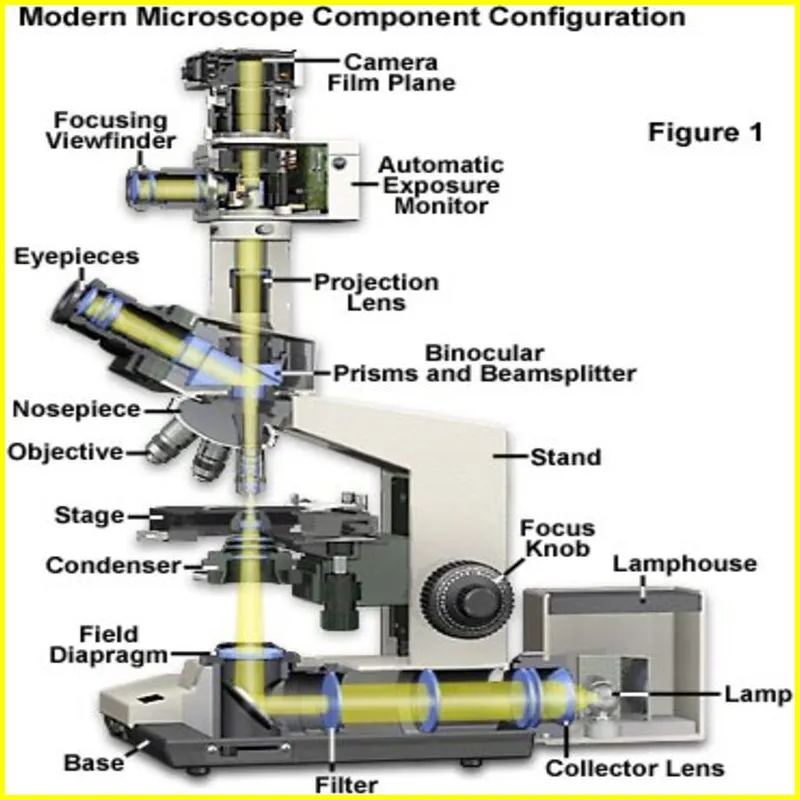
What are the 12 parts of compound microscope?
Some of the important parts are base or foot, pillar, arm, tilt joint, stage, clip, diaphragm, body tube, nose piece, coarse adjustment knob and fine adjustment knob.
What are the 14 parts of compound microscope?
Each part of the microscope has a different function.
Eyepiece or ocular lens. The eyepiece lens magnifies the image of the specimen.
Eyepiece tube or body tube. The tube holds the eyepiece.
Nosepiece.
objective lenses.
arm.
stage.
stage clips.
diaphragm.
What are the parts and functions of a compound light microscope?
The light source provides the necessary light to view the sample. This platform is where the slides are placed. The nosepiece holds the objective lens. The eyepiece (ocular) is the first lens you look through (usually around 10x) when you use a compound microscope.
What are the 10 parts of compound microscope?
Some of the main parts of a compound microscope are
foot or base. It is a U-shaped structure and supports the entire weight of the compound microscope.
column. This is a vertical projection.
arm. The entire microscope is controlled by a strong and curved structure known as the arm.
stage.
tilt joint.
clip.
diaphragm.
Nose piece.




